Dolmabahce Palace, an iconic landmark in Istanbul, Turkey, was commissioned by Sultan Abdulmecid I. This luxurious palace, built to serve as the central office for the Ottoman Empire, includes over 285 beautifully decorated rooms, featuring sparkling Dolmabahce chandeliers and elaborate ceilings. Its gardens offer spectacular views of the Bosphorus Strait, making it a key destination for visitors seeking to experience the opulence of Ottoman architecture. This section explores the rich history of Dolmabahce Palace, from its initial construction in 1856 to its role today as a historical museum and cultural site.

Sultan Abdulmecid I initiated the construction of Dolmabahce Palace, envisioning it as a modern replacement for the old Beylerbeyi Palace. Construction of Dolmabahce Palace began, under the guidance of the renowned Ottoman architects Garabet Amira Balyan and his son Nikogos Balyan.
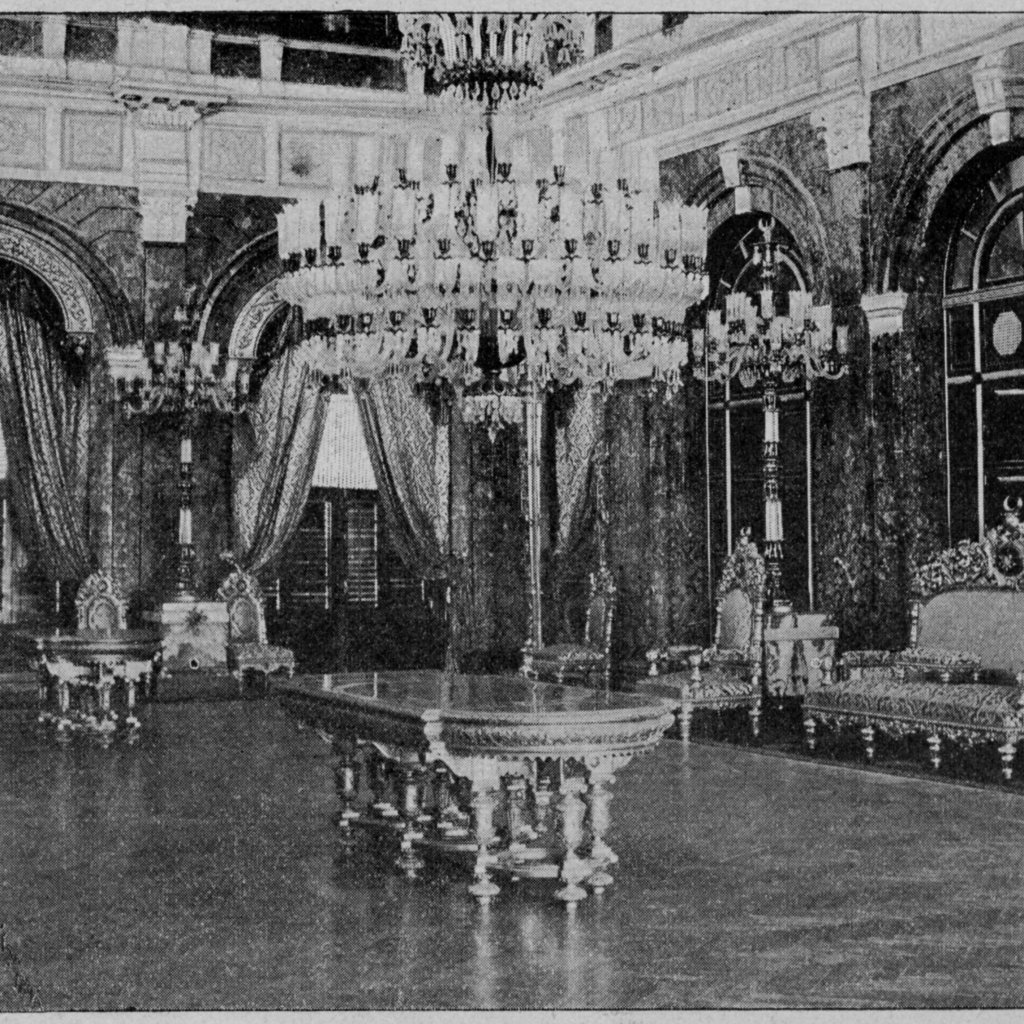

The construction of Dolmabahce Palace was completed, and it became the central administrative hub of the Ottoman Empire.
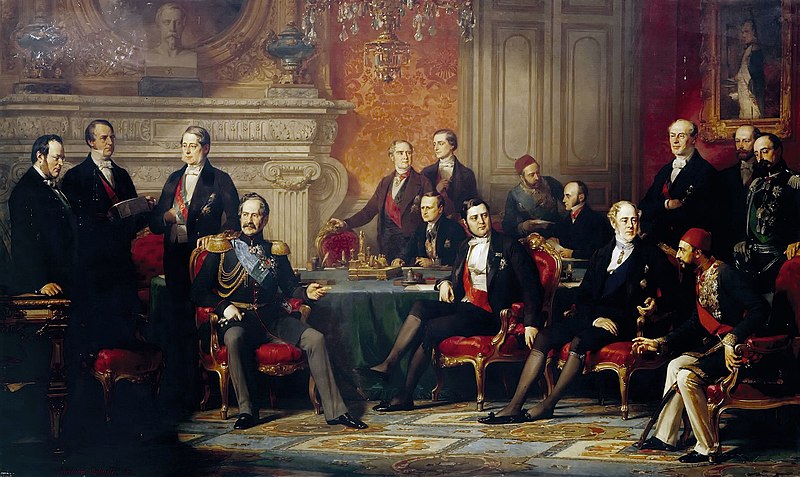

Dolmabahce Palace was the site where the Treaty of Paris was signed, marking the first major international agreement hosted at the palace.
The Hagia Sophia Church Mosque we recognize today was erected by Emperor Justinian I and consecrated in 537 AD. This marked the creation of the third and most magnificent version of the Hagia Sophia.
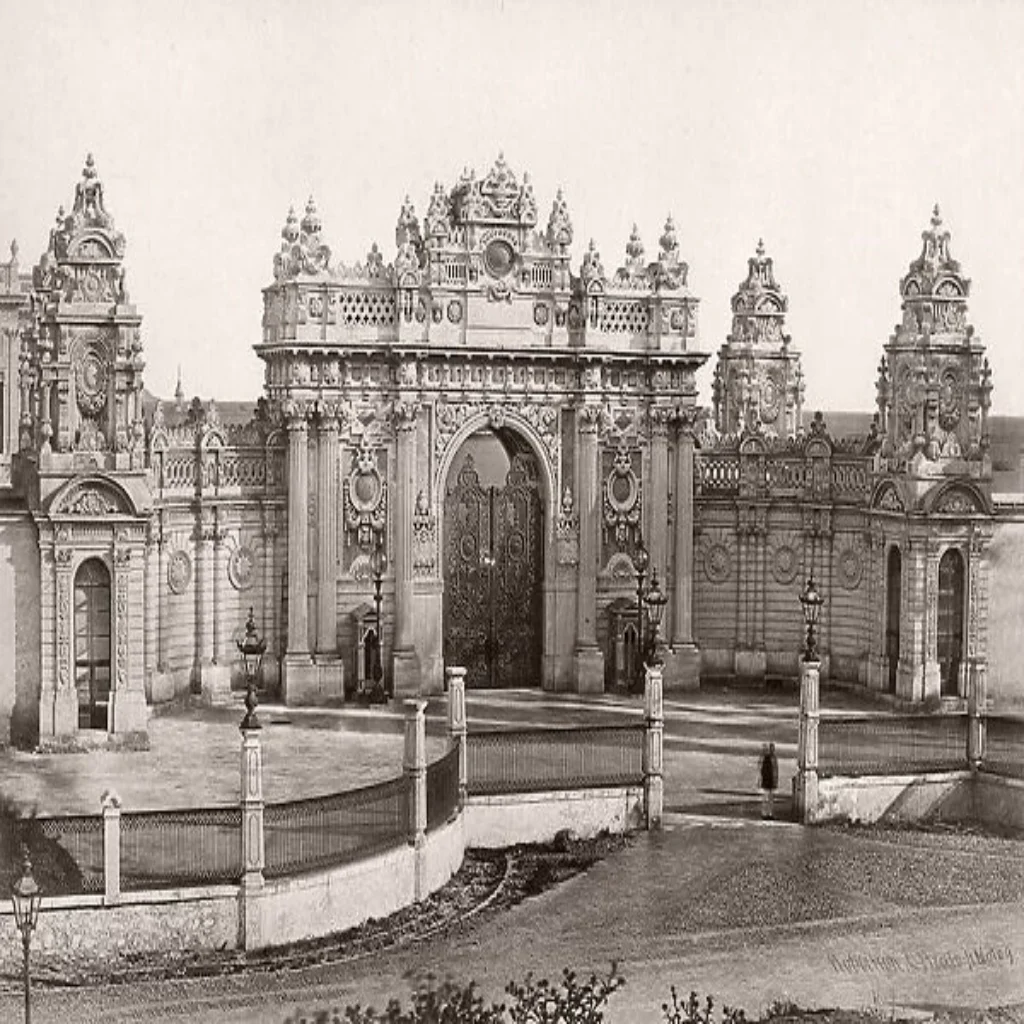

Following the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, Dolmabahce Palace was taken over by the new Turkish Republic and was designated as the new presidential palace.
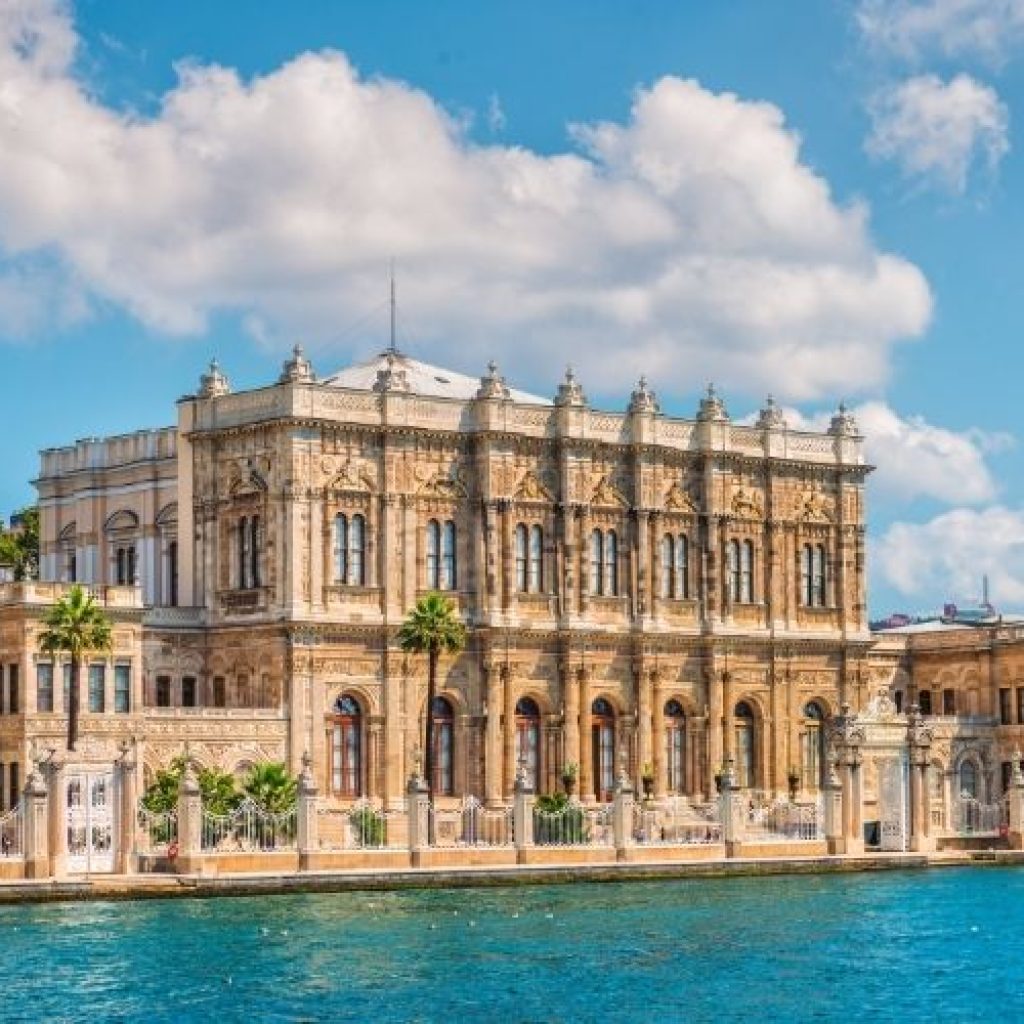

Dolmabahce Palace was converted into a museum, opened to the public to enrich understanding of its historical significance.
The construction of Dolmabahce Palace began earnestly in 1846 after the decree by Sultan Abdulmecid. The architects Garabet and Nigogayos Balyan designed the palace in a magnificent blend of Neoclassical, Baroque, and traditional Ottoman styles, which are evident throughout the structure.
Upon its completion, Dolmabahce Palace took over from Topkapi Palace as the new main administrative center of the Ottoman Empire, hosting six Ottoman Sultans and a Caliph until the empire’s dissolution in 1922.
In 1922, with the establishment of the Turkish Republic, Dolmabahce Palace transitioned to a new role, becoming the residence of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, where he hosted numerous international dignitaries and led efforts to modernize Turkey.
Transformed into a museum in 1984, Dolmabahce Palace now serves as a portal to the past, allowing visitors to explore its opulent rooms and halls, and learn about the rich tapestry of Turkish and Ottoman history.
Today, Dolmabahce Palace stands as a monument to the lavish lifestyle of the Ottoman elite. Its Crystal Staircase, huge Dolmabahce Palace chandelier, and the grand Ceremonial Hall are just some of the highlights that draw visitors from around the world. The palace’s strategic location along the Bosphorus Strait offers unmatched views, making it a must-visit for anyone traveling to Istanbul.
Dolmabahce Palace was built in the mid-19th century, making it over 160 years old.
The palace was designed by the famous Ottoman architects, Garabet Amira Balyan and his son Nikogos Balyan.
The palace features a blend of Baroque, Rococo, and Neoclassical styles, merged with traditional Ottoman architectural elements. Here are more information about the architecture.
Absolutely, for its historical significance, stunning architecture, and beautiful gardens, Dolmabahce Palace is a must-visit landmark in Istanbul.
Visitors can tour the luxurious interiors, including the famed Crystal Staircase and the vast Ceremonial Hall with its grand chandelier. The palace’s well-manicured gardens offer a peaceful retreat with stunning views of the Bosphorus. Here for more information on what is inside.
Dolmabahce Palace is located along the European shore of the Bosphorus Strait in the Besiktas district of Istanbul, Turkey. Look up the detailed directions.
The palace is accessible via public transport in Istanbul. Visitors can take a bus, tram, or ferry to Besiktas and then walk to the palace. Look up the detailed directions.
Dolmabahce Palace is open from 9:00 to 18:00, Tuesday to Sunday. It is closed on Mondays. Here the opening hours.
Entry tickets for Dolmabahce Palace start at approximately €29 for basic admission. Prices may vary for different tours and visitor experiences.
Yes, guided tours are available and are an excellent way to learn about the palace’s rich history and significance. Audio guides are also available for those who prefer self-guided tours.
Dolmabahce Palace served as the main administrative center of the Ottoman Empire from 1856 until 1922 and was later used as presidential palace. It is historically significant for its role in the transition from empire to republic. Here the history.
Photography inside Dolmabahce Palace is restricted to protect the interiors. Photos are allowed in the gardens and exterior areas.
